How Much Current Does An Arduino Nano Draw

 Hi Friends! I hope you are doing fine. Today, I am going to give you a detailed Introduction to Arduino Nano . We will also discuss Arduino Nano Pinout, datasheet, drivers & applications. It is a Microcontroller board developed past arduino.cc and based on Atmega328p / Atmega168.
Hi Friends! I hope you are doing fine. Today, I am going to give you a detailed Introduction to Arduino Nano . We will also discuss Arduino Nano Pinout, datasheet, drivers & applications. It is a Microcontroller board developed past arduino.cc and based on Atmega328p / Atmega168.
Arduino boards are widely used in robotics, embedded systems, automation, Cyberspace of Things(IoT) and electronics projects. These boards were initially introduced for the students and not-technical users but nowadays Arduino boards are widely used in industrial projects.
Any kind of technical support and assist is readily provided past the Arduino community. I have as well designed this video tutorial on Arduino Nano:
- Here's the figure showing keypoints of Arduino Nano:
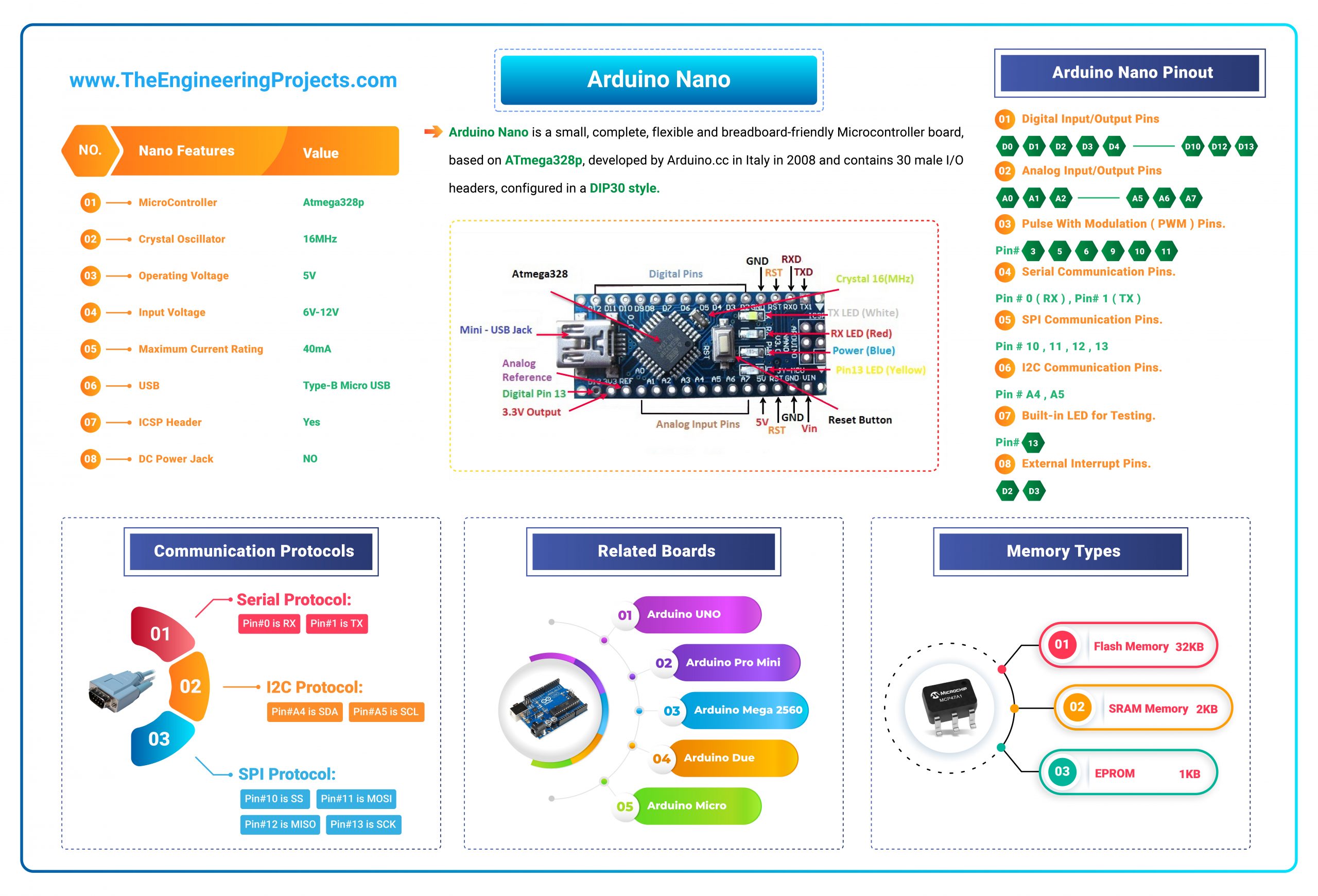
- Here's the tabular array showing important features of Arduino Nano:
| No. | Nano Features | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microcontroller | Atmega328p |
| 2 | Crystal Oscillator | 16MHz |
| iii | Operating Voltage | 5V |
| four | Input Voltage | 6V-12V |
| five | Maximum Electric current Rating | 40mA |
| 6 | USB | Type-B Micro USB |
| 7 | ICSP Header | Yes |
| eight | DC Power Jack | No |
- Here'due south the quick overview of Arduino Nano Pinout:
| No. | Pin Number | Pin Clarification |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | D0 – D13 | Digital Input / Output Pins. |
| two | A0 – A7 | Analog Input / Output Pins. |
| iii | Pin # 3, v, half-dozen, nine, x, 11 | Pulse Width Modulation ( PWM ) Pins. |
| 4 | Pin # 0 (RX) , Pin # ane (TX) | Serial Communication Pins. |
| 5 | Pin # 10, xi, 12, 13 | SPI Advice Pins. |
| 6 | Pin # A4, A5 | I2C Communication Pins. |
| 7 | Pin # xiii | Built-In LED for Testing. |
| eight | D2 & D3 | External Interrupt Pins. |
- Arduino Nano offers three types of communications protocols, shown in the beneath table:
| No. | Advice Protocols | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | Serial Port | 1 (Pin#0 is RX, Pin#1 is TX). |
| 7 | I2C Port | 1 (Pin#A4 is SDA, Pin#A5 is SCL). |
| 8 | SPI Port | ane (Pivot#10 is SS, Pin#11 is MOSI, Pivot#12 is MISO, Pivot#13 is SCK). |
- Hither'southward the retention details present in Arduino Nano:
| No. | Retention Type | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Flash Retentivity | 32KB |
| eight | SRAM Retentivity | 2KB |
| 7 | EEPROM | 1KB |
Introduction to Arduino Nano
-
 Arduino Nano is a small, complete, flexible and breadboard-friendly Microcontroller lath, based on ATmega328p , developed by Arduino.cc in Italy in 2008 and contains 30 male person I/O headers, configured in a DIP30 style .
Arduino Nano is a small, complete, flexible and breadboard-friendly Microcontroller lath, based on ATmega328p , developed by Arduino.cc in Italy in 2008 and contains 30 male person I/O headers, configured in a DIP30 style . - Arduino Nano Pinout contains 14 digital pins, viii analog Pins, ii Reset Pins & 6 Power Pins.
- It is programmed using Arduino IDE , which tin can be downloaded from Arduino Official site.
- Arduino Nano is simply a smaller version of Arduino UNO, thus both have almost the same functionalities.
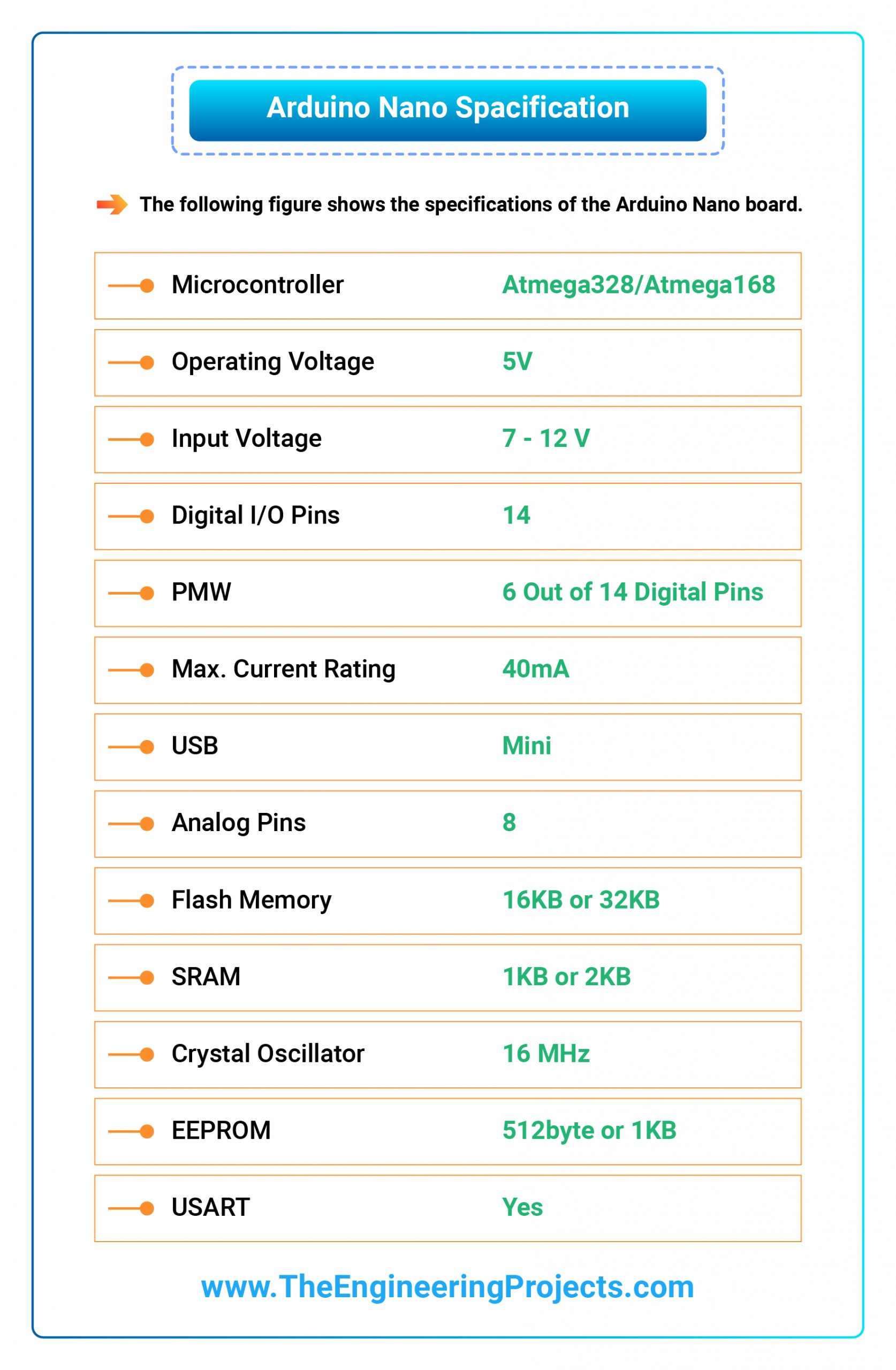
- It comes with an operating voltage of 5V , however, the input voltage can vary from 7 to 12V .
- Arduino Nano'southward maximum current rating is 40mA , so the load attached to its pins shouldn't draw current more than than that.
- Each of these Digital & Analog Pins is assigned with multiple functions merely their master part is to be configured as Input/Output .
- Arduino Pins are acted as Input Pins when they are interfaced with sensors, simply if you are driving some load then we demand to use them as an Output Pin .
- Functions like pinMode() and digitalWrite() are used to control the operations of digital pins while analogRead() is used to command analog pins.
- The analog pins come with a total resolution of 10-bits which measures the value from 0 to 5V.
- Arduino Nano comes with a crystal oscillator of frequency xvi MHz . Information technology is used to produce a clock of precise frequency using constant voltage.
- At that place is one limitation of using Arduino Nano i.e. it doesn't come with a DC power jack , which means you tin not supply an external ability source through a battery.
- This board doesn't use standard USB for connectedness with a computer, instead, information technology comes with Type-B Micro USB .
- The tiny size and breadboard-friendly nature make this device an ideal option for most applications where the size of the electronic components is of great concern.
- Flash retentivity is 16KB or 32KB that all depends on the Atmega lath i.e Atmega168 comes with 16KB of flash memory while Atmega328 comes with a flash memory of 32KB. Flash memory is used for storing code. The 2KB of memory out of total wink memory is used for a bootloader.
- The SRAM memory of 2KB is present in Arduino Nano.
- Arduino Nano has an EEPROM memory of 1KB .
- You can download Arduino Nano Datasheet by clicking the below push:
Download Arduino Nano Datasheet
- The post-obit figure shows the specifications of the Arduino Nano board.
- Information technology is programmed using Arduino IDE which is an Integrated Evolution Environment that runs both offline and online.
- No prior arrangements are required to run the board. All y'all demand is a board, mini USB cable and Arduino IDE software installed on the calculator.
- USB cable is used to transfer the program from the computer to the board.
- No separate burner is required to compile and burn the programme every bit this board comes with a built-in boot-loader.
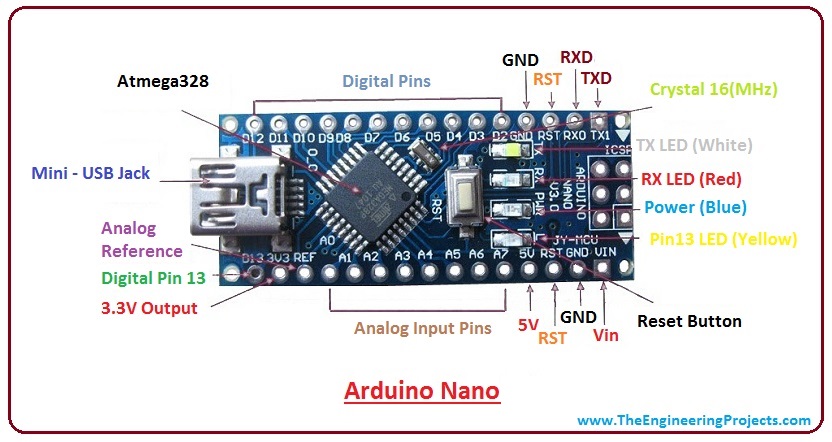
Now, allow's have a await at Arduino Nano Pinout in detail:
Arduino Nano Pinout
- The following figure shows the pinout of the Arduino Nano Board:
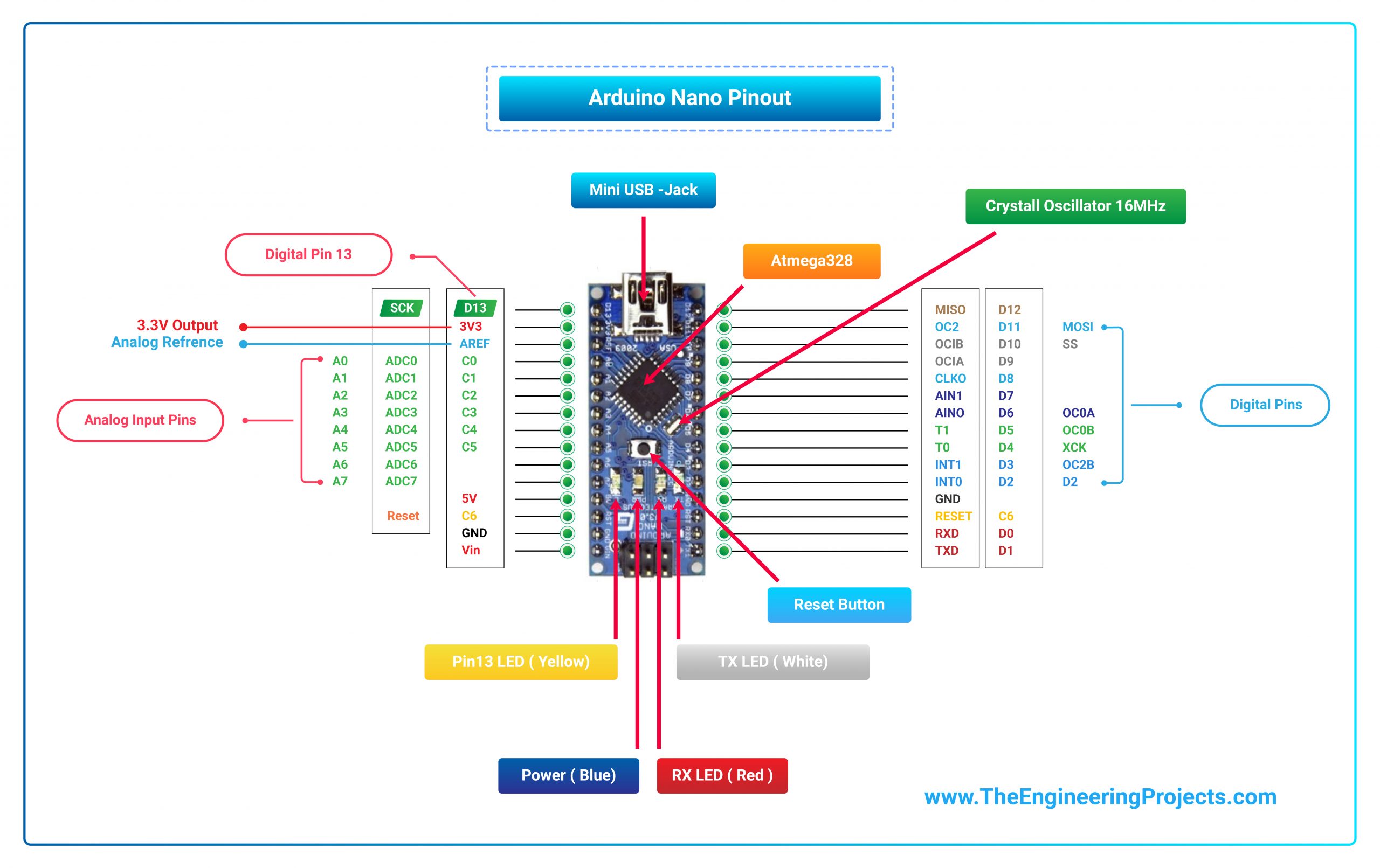
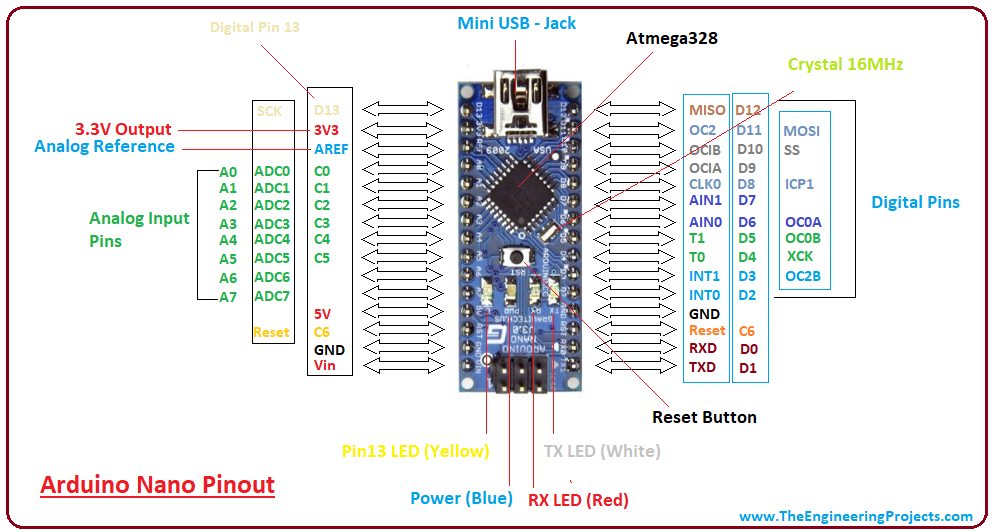
- Each pin on the Nano board comes with a specific office associated with it.
- Nosotros can see the analog pins that can be used as an analog to a digital converter, where A4 and A5 pins can also exist used for I2C communication.
- Similarly, there are fourteen digital pins, out of which vi pins are used for generating PWM.
Allow'due south have a wait at the Arduino Nano Pinout in detail:
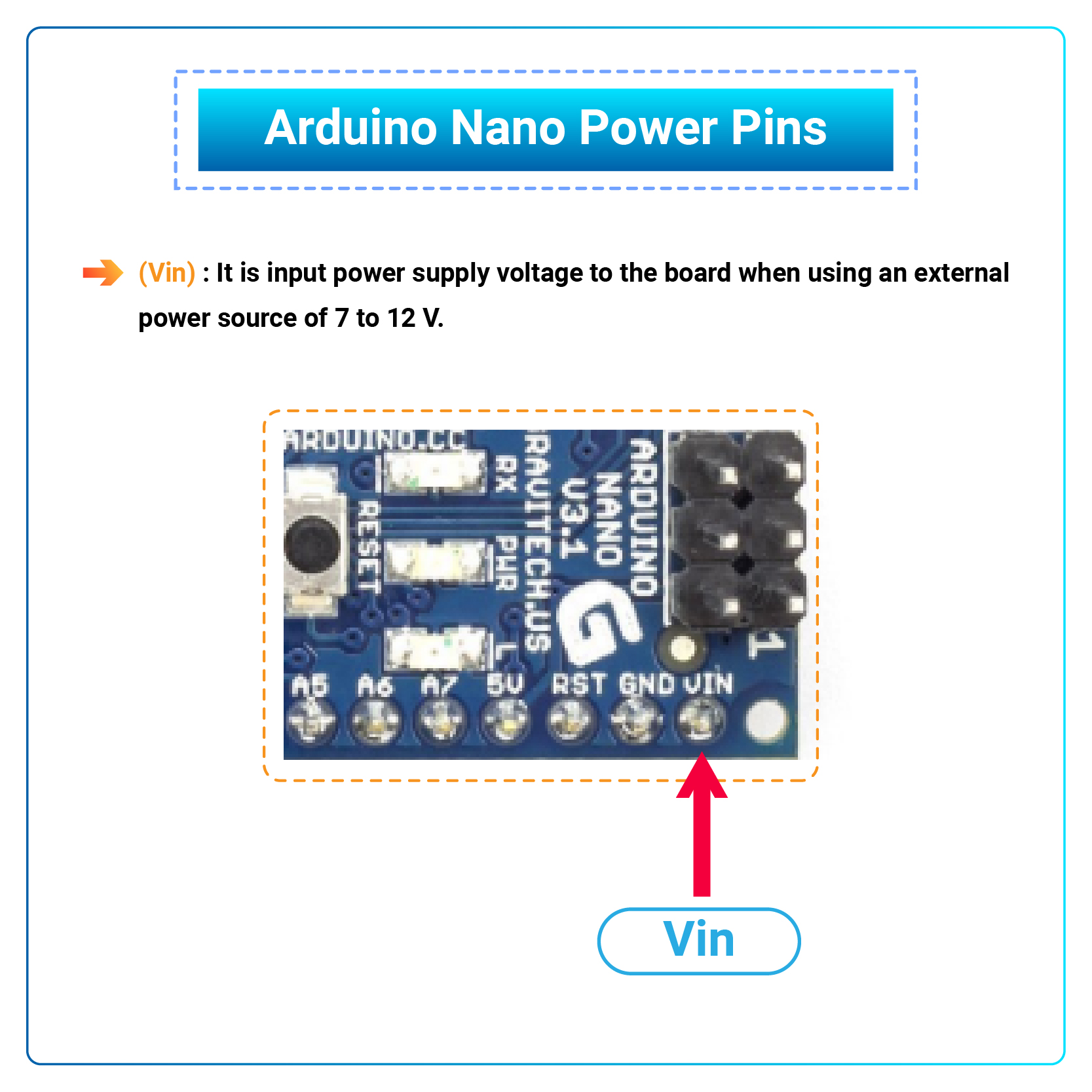
Arduino Nano Power Pins
- Vin: Information technology is input power supply voltage to the lath when using an external ability source of 7 to 12 V.
- 5V: It is a regulated power supply voltage of the lath that is used to power the controller and other components placed on the lath.

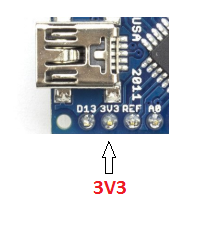
- 3V3: This is a minimum voltage generated by the voltage regulator on the nano board.
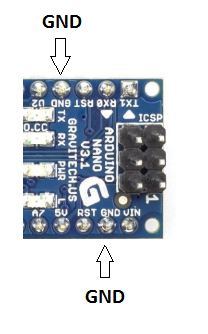
- GND Pin: These are the ground pins on the board.
- In that location are multiple basis pins on the board that can be interfaced appropriately when more than one basis pin is required.
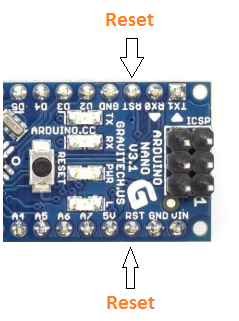
Arduino Nano Office Pins
- Reset Pivot: Arduino Nano has two reset pins incorporated on the lath, making any of these Reset pins LOW volition reset the microcontroller.
- Pin#13: A built-in LED is continued to pivot#13 of nano board.
- This LED is used to cheque the lath i.e. it'southward working fine or not.
- AREF: This pin is used as a reference voltage for the input voltage.
Arduino Nano I/O Pins
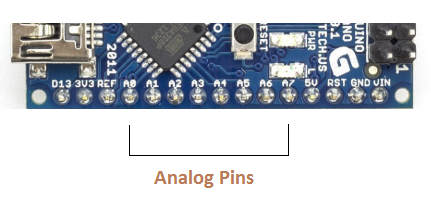
- Analog Pins: There are eight analog pins on the board marked as A0 – A7 .
- These pins are used to mensurate the analog voltage ranging between 0 to 5V .
- Digital Pins : Arduino Nano has xiv digital pins starting from D0 to D13.
- These digital pins are used for interfacing third-party digital sensors and modules with Nano lath.
- PWM Pins: Arduino Nano has 6 PWM pins, which are Pin#3, 5, 6, 9, 10 and xi. (All are digital pins)
- These pins are used to generate an 8-flake PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) bespeak.
- External Interrupts: Pin#2 and iii are used for generating external interrupts ordinarily used in case of emergency, when nosotros need to stop the main program and telephone call important instructions.
- The main programme resumes once interrupt instruction is called and executed.
Nano Pinout for Communication Protocols
- Series Pins: These pins are used for series communication where:
- Pivot#0 is RX used for receiving series data.
- Pin#one is Tx used for transmitting series information.

- SPI Protocol: 4 pins 10(SS->Slave Select), eleven(MOSI -> Chief Out Slave In), 12(MISO -> Master In Slave Out) and 13(SCK -> Series Clock) are used for SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) Protocol.
- SPI is an interface bus and is mainly used to transfer data between microcontrollers and other peripherals like sensors, registers, and SD cards.
- I2C Protocol: I2C communication is developed using A4 and A5 pins, where A4 represents the serial data line (SDA) which carries the data and A5 represents the serial clock line (SCL) which is a clock signal, generated past the master device, used for data synchronization betwixt the devices on an I2C bus.
Arduino Nano Programming & Communication
- The Nano lath comes with the ability to prepare communication with other controllers and computers.
- The serial communication is carried out by the digital pins, Pivot 0(Rx) and Pin 1(Tx) where Rx is used for receiving data and Tx is used for the transmission of data.
- The serial monitor is added to the Arduino IDE, which is used to transmit textual data to or from the board.
- FTDI drivers are also included in the software which behaves every bit a virtual com port to the software.
- The Tx and Rx pins come with an LED which blinks every bit the data is transmitted between FTDI and USB connection to the computer.
- Arduino Software Serial Library is used for carrying out series communication between the board and the estimator.
- Apart from serial communication the Nano board also supports I2C and SPI advice. The Wire Library within the Arduino Software is accessed to utilize the I2C bus.
- The Arduino Nano is programmed by Arduino Software called IDE which is a common software used for most all types of board available. Merely download the software and select the lath y'all are using.
- Uploading code to Arduino Nano is quite simple, as there's no demand to use any external burner to compile and burn the program into the controller and yous tin can likewise upload code by using ICSP (In-excursion serial programming header).
- Arduino board software is equally compatible with Windows, Linux or MAC, even so, Windows are preferred to utilize.
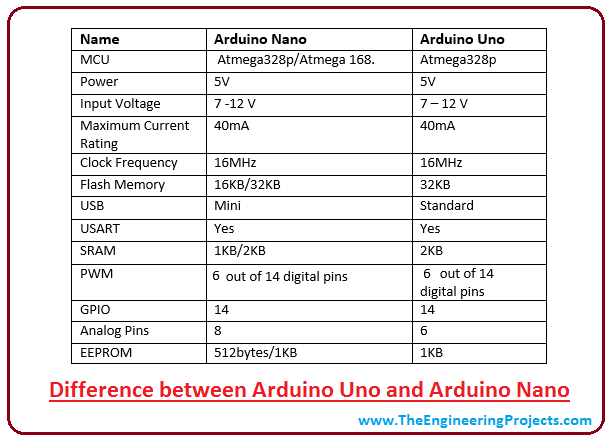
Arduino Uno Vs Arduino Nano
- Both Arduino Uno and Arduino Nano come with the same functionality with little difference in terms of PCB layout, size and class cistron.
- Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on Atmega328 and comes with fourteen digital I/O pins out of which half-dozen are PWM. At that place are 6 analog pins incorporated on the lath. This board comes with everything required to support the microcontroller like a USB connection, a Power jack, 16MHz oscillator, reset button and ICSP header. Yous don't require an extra peripheral with the board to go far work for automation.
- Information technology is a complete prepare to use device that requires no prior technical skills to go hands-on feel with it. You can power it by using a DC power jack, battery or simply plug it into the computer using a USB cable to get started.
- Arduino Nano is modest and compact as compared to Arduino Uno. It lacks the DC power jack and comes with Mini USB support instead of regular USB. Besides, the Nano lath comes with two extra analog pins i.e. 8 pins as compared to vi analog pins in the Uno board. Nano board is breadboard friendly while Uno board lacks this property.
- However, both devices run at 5V, come with a current rating of 40mA, and 16MHz of the clock frequency.
Applications of Arduino Nano
Arduino Nano is a very useful device that comes with a wide range of applications and covers less space as compared to other Arduino boards. Breadboard-friendly nature makes it stand up out from other boards. Following are the main applications of Arduino Nano:
- Engineering Students' Projects.
- Medical Instruments
- Industrial Automation
- Android Applications
- GSM Based Projects
- Embedded Systems
- Automation and Robotics
- Dwelling house Automation and Defense Systems
- Virtual Reality Applications
That'due south all for today. I hope yous accept got a clear idea nigh the Nano lath. However, if nevertheless you feel skeptical or have whatsoever questions, y'all can arroyo me in the comment section beneath. I'd love to help you according to the best of my knowledge and expertise. Experience free to proceed the states updated with your valuable feedback and suggestions, they help united states of america provide y'all quality work that resonates with your requirements and allows you to continue coming back for what nosotros accept to offer. Cheers for reading the article.
Source: https://www.theengineeringprojects.com/2018/06/introduction-to-arduino-nano.html
Posted by: cookshiled.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Much Current Does An Arduino Nano Draw"
Post a Comment